Run your business
Basics of small business accounting in 2023
What is accounting?
Accounting for a small business is the process of tracking, classifying, recording, summarizing and analyzing the financial transactions. Accounting helps business owners, investors and creditors understand and assess the health of the business. It includes recording income, expenses, liabilities and assets. In short, accounting is the way of managing finances of a business. And accounting is not optional..it is essential for all businesses to maintain appropriate books and accounts to stay compliant with tax laws, securities laws, and other regulations. Negligence can result in the businesses having to pay penalties and fines.
Small business accounting can be done manually or with the help of accounting software. It is always recommended to hire a CPA as nothing can replace professional help and ensuring correctly.

Difference between accounting and book keeping
This is a very common question in every business owner’s mind – what is the difference between accounting and bookkeeping and can the terms be used interchangeably. While bookkeeping and accounting are two closely related, but they have different purpose and meaning.
Small business bookkeeping is the process of recording and classifying every financial transaction of the business in an organized fashion. It involves maintaining accurate record of all monetary transactions of the business.
Accounting on the other hand is a looking at the financial picture through a wider lens. It involves using the financial data to to assess the financial health of the business. Accounting comprises of bookkeeping and other aspects of financial management, so essentially bookkeeping is a subset of accounting. Generating balance sheets, income statements and profit & loss statements is all part of accounting.
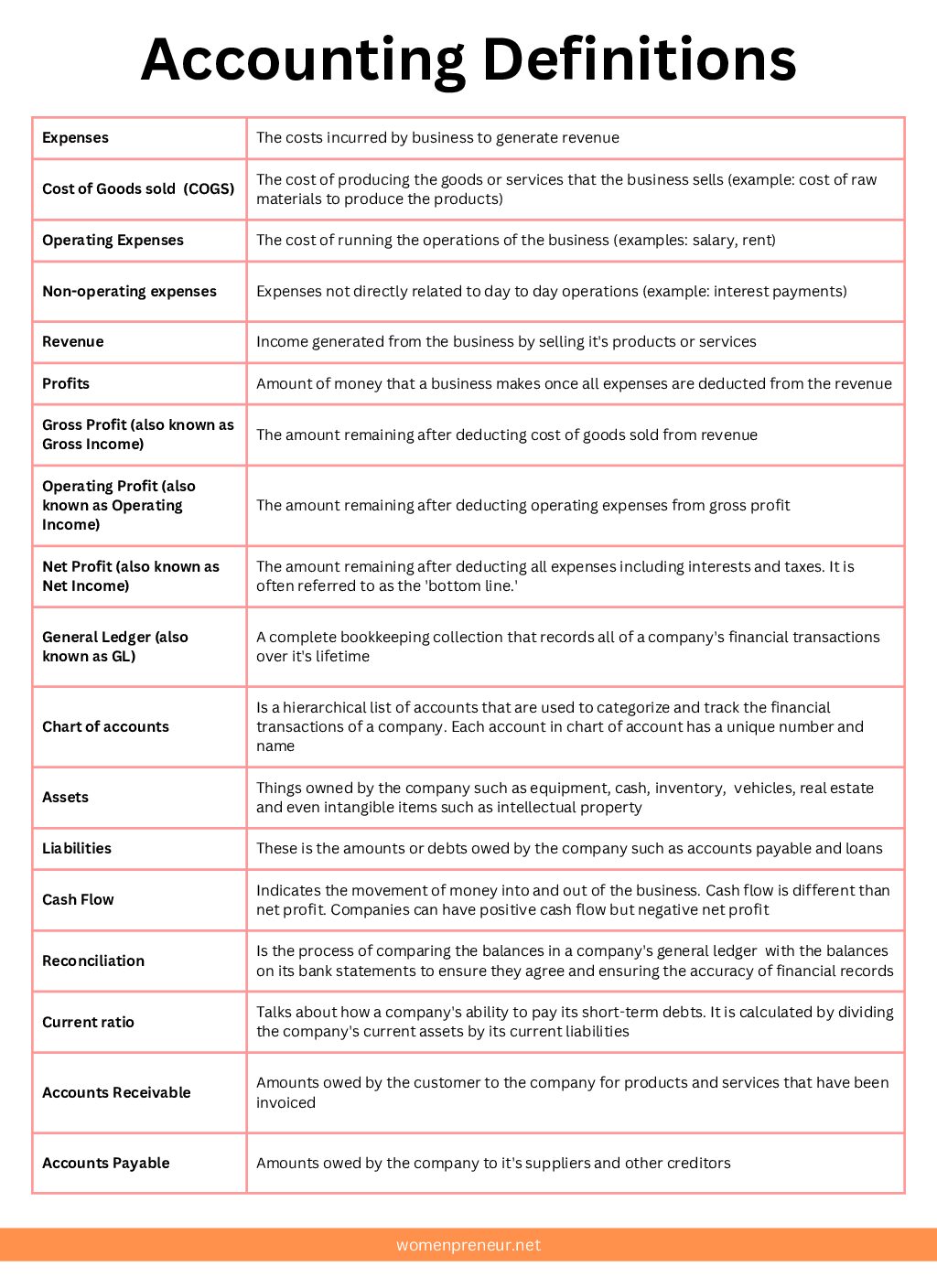
Basic terms in accounting
Here are the key terms in accounting with simple explanations for each that every business owner should know.
Expenses
The costs incurred by business to generate revenue. Expenses are categorized into three types:
-
Cost of Goods sold (COGS) – The cost of producing the goods or services that the business sells (example: cost of raw materials to produce the products)
-
Operating Expenses – The cost of running the operations of the business (examples are salary, rent)
-
Non operating expenses – Expenses not directly related to day to day operations (example: interest payments)
Revenue
Income generated from the business by selling it’s products or services
Profits
Amount of money that a business makes once all expenses are deducted from the revenue.
-
Gross Profit (also called Gross Income or Gross Margins) – The amount remaining after deducting cost of goods sold from revenue
-
Operating Profit (also called Operating Income)- The amount remaining after deducting operating expenses from gross profit.
-
Net Profit (also called Net Income) – The amount remaining after deducting all expenses including interests and taxes. It is often referred to as the ‘bottom line.’
General Ledger (also known as GL)
A complete bookkeeping collection that records all of a company’s financial transactions over it’s lifetime.
Chart of Accounts
Is a hierarchical list of accounts that are used to categorize and track the financial transactions of a company. Each account in chart of account has a unique number and name
Assets
Things owned by the company such as equipment, cash, inventory, vehicles, real estate and even intangible items such as intellectual property.
Liabilities
These is the amounts or debts owed by the company such as accounts payable and loans
Cash Flow
Indicates the movement of money into and out of the business. Cash flow is different than net profit. Companies can have positive cash flow but negative net profit.
Reconciliation
Is the process of comparing the balances in a company’s general ledger with the balances on its bank statements to ensure they agree and ensuring the accuracy of financial records.
Current ratio
Talks about how a company’s ability to pay its short-term debts. It is calculated by dividing the company’s current assets by its current liabilities. Read more about current ration in our blog about Balance Sheets.
Accounts Receivable
Amounts owed by the customer to the company for products and services that have been invoiced
Accounts Payable
Amounts owed by the company to it’s suppliers and other creditors
Here’s a handy image that includes all the key definitions in a table.
How to set up basic accounting for small business
Now that you understand the key terms in accounting, here are the simple steps you need to consider to create a basic but solid accounting framework for your small business.
By the time you are ready to set up accounting for your business, your business should already have a legal structure.
Step 1 : Set up a business bank account
Setting up your business bank account is one of the first steps to setting your accounting system. LLCs, partnerships and corporations require you to have a business bank account for all business financial transactions. Sole proprietorships are not required to have a business bank account but it is highly recommended that businesses always have their business bank accounts separate than a personal ones. This will make it much easier to track your business income and expenses.
Step 2: Determining your accounting method
-
There are two types of accounting methods – cash basis accounting and accrual basis accounting.
-
-
Businesses using cash basis accounting record transactions when cash is received or paid. This is the simplest method of accounting but there can be circumstances where it is not the most accurate because it does not take into account revenue that has not been received and any expenses that have not been paid yet. It looks at cash transactions in real time.
-
Accrual basis accounting records transactions when they occur, regardless of when cash is received or paid. So for the business, the revenue is recorded when it earned and not when the cash is received for the transaction. Same goes for expenses which are recorded when the expense is made and not when the cash is paid. Of the two, accrual basis accounting is the more complex one.
-
-
Step 3: Creating the Chart of accounts
As mentioned above, chart of accounts is the list of accounts used to classify and track financial transactions for your business. Creating chart of accounts involves identifying the types of accounts needed for the business. Once you have a list ready, assign a unique name and code for each account. Chart of accounts are set up in a hierarchical structure so they can be grouped together in categories. Example – you may have an account for Employee Engagement and separate accounts underneath it each for Travel, Meals, and Team Building.
Step 4: Expense tracking
It is essential to track all your business expenses and file receipts for those transactions. A great practice is to ensure you are using your business credit or debit card for all expenses pertaining to your business and safely storing all your receipts by scanning and saving on a drive.
Step 5: Set up bookkeeping system
Bookkeeping involves categorizing the receipts appropriately under the right category or accounts. Business owners canuse manual bookkeeping to record their transactions though it can be time-consuming and risky if not done correctly. This involves maintaining a journal or ledger of all business transactions. Purchasing a bookkeeping or accounting software can make things very easy and it is definitely a way more efficient option.

Step 6: Set up a payment system
This involves determining how customers will pay you for your services. Will it be via cash, credit card and/or checks. It also includes selecting a payment processor. Payment processors enable small business merchants to accept payments from various payment sources such as credit cards and debit cards.
Step 7: Set up Payroll
Selecting a good payroll provider is one of the most key decisions for your business. Some business owners manage payroll manually but that is exceedingly time consuming and risk prone. Determining employee status, payroll schedule, and getting a strong handle on the taxes, contributions and deductions for your employees are all essential considerations. Gusto is a great choice for online payroll provider for small businesses.
Step 8: Determine tax requirements
It is essential that every small business owner understands their federal, state and local tax obligations. These differ based on the legal entity or structure of your business. The IRS page (https://www.irs.gov/businesses) summarizes the requirements but I highly recommend taking guidance from a tax professional or CPA.
Step 9: Set up Sales Tax
Determining whether your business is required to collect sales tax, applying for a sales tax permit, creating a system for collecting sales tax from customers on the goods and services they buy from you, and paying sales tax to the state in a timely fashion are all things that need to be set up for your small business.
Step 10: Familiarity with financial reports
Getting acquainted with the key accounting reports is important to be able to assess the health of your business. Some key reports that every small business owner should be well acquainted with are Balance Reports, Income Statement, and Profit & Loss statement
Do I need a CPA?
The answer to this question depends on how complex your business is and how comfortable you are with finances and accounting. However you choose to move forward, setting up accounting right from the very start is crucial to your business’s success and in ensuring you are doing everything in compliance with the state and federal laws.
To summarize, it is imperative to get the correct framework in place for accounting right when you are setting up your business. This way everything that follows
You can download a free guide with the steps for setting up Accounting for your small business.


